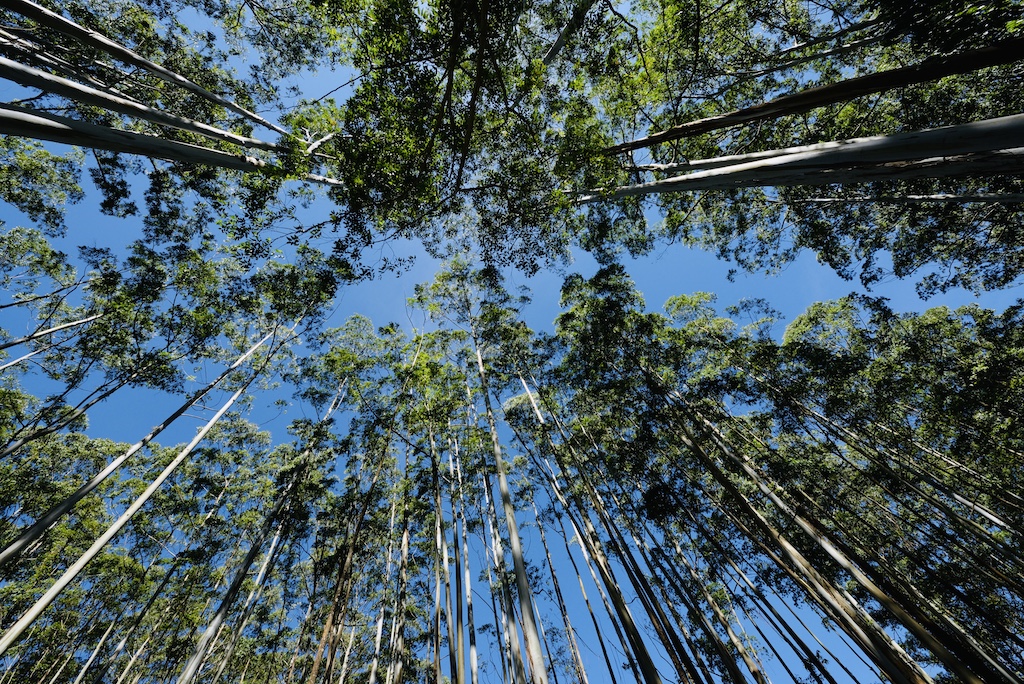
Photography offers a wide range of creative possibilities, and photographers often explore various topics based on their interests, style, and expertise. Here are some popular and intriguing photography topics that photographers often focus on:
1. Landscape Photography:
- Landscape photography requires patience, detailing, and an understanding of the natural world. Capturing scenic natural landscapes, seascapes, mountains, valleys, bodies of water, forests, and other natural features. This genre often emphasizes composition, lighting, and capturing the beauty of nature. It’s popular among both professional and amateur photographers, as it allows for creative expression and a connection with nature.
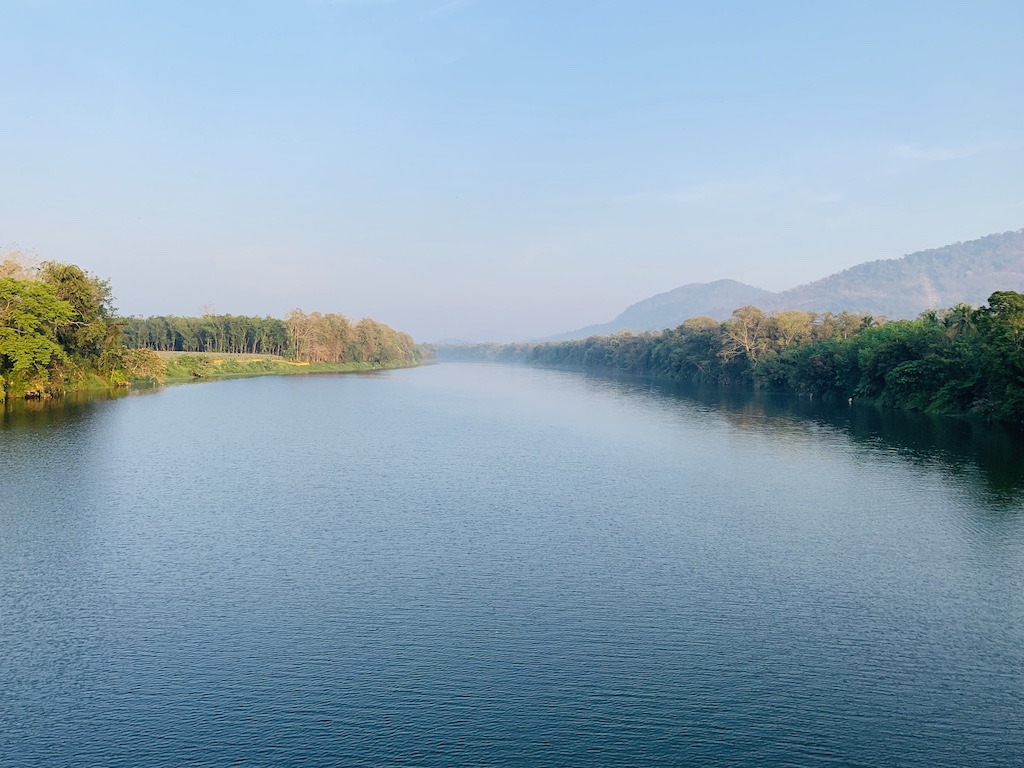

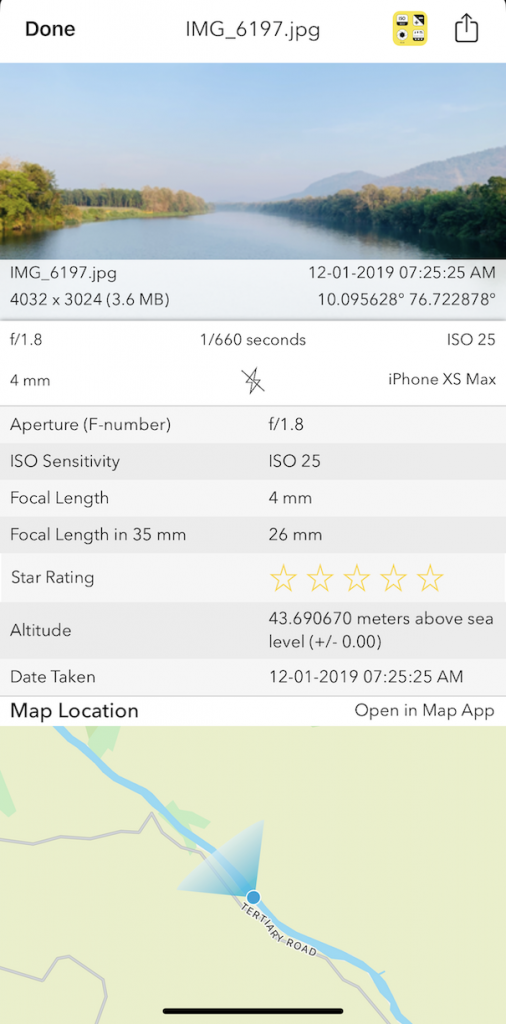
Above image metadata displayed using EXIF Viewer by Fluntro App.
Open Exif Viewer by Fluntro App
Viewing EXIF Metadata after transferring photos to your device. Checkout :- What is Exif Metadata in Photography?
Techniques commonly used in landscape photography include:
- Composition: Thoughtful arrangement of elements within the frame to create a visually pleasing and balanced image. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and framing are common compositional techniques.
- Lighting: The quality of light greatly affects the mood and atmosphere of the photograph. Golden hours (shortly after sunrise and before sunset) are often preferred for their warm and soft lighting.
- Depth of Field: Adjusting the aperture to control the depth of field, allowing for both foreground and background elements to be in focus or creating a shallow depth of field to isolate specific subjects.
- Framing: Using natural elements like trees, rocks, or archways to frame the main subject, adding depth and context to the image.
- Foreground Interest: Incorporating interesting foreground elements can add depth and a sense of scale to the photograph, drawing the viewer’s eye into the scene.
- Use of Filters: Graduated neutral density filters, polarizing filters, and other types of filters are often used to control exposure, enhance colors, reduce reflections, and balance lighting.
- Tripods: Using a tripod helps ensure sharpness in images, especially in low-light conditions, and allows for longer exposure times.
- Perspective: Experimenting with different angles and heights can lead to unique and engaging compositions.
- Post-Processing: Editing software can be used to enhance colors, adjust contrast, correct exposure, and remove distractions, while still maintaining a natural and realistic look.
Types of lenses commonly used for landscape photography:
- Wide-Angle Lenses: Wide-angle lenses, typically in the range of 10mm to 35mm focal length for full-frame cameras, are popular for capturing expansive landscapes. They allow you to include a large portion of the scene in the frame, making them great for vast vistas, sweeping skies, and foreground-background compositions. Ultra-wide-angle lenses, such as fisheye lenses, can also add a unique perspective to landscapes.
- Standard Zoom Lenses: Standard zoom lenses in the range of 24mm to 70mm are versatile options for landscapes. They provide a bit more zoom compared to wide-angle lenses, allowing for some flexibility in composition and the ability to isolate specific elements in the scene.
- Telephoto Zoom Lenses: While not the most common choice for landscapes, telephoto zoom lenses (70mm and beyond) can be used to capture compressed perspectives and bring distant subjects closer. They are particularly useful for capturing specific details in landscapes, like isolated mountains or intricate patterns.
- Prime Lenses: Prime lenses offer a fixed focal length and tend to have excellent optical quality. Wide-angle prime lenses are often used for landscapes, as they can produce very sharp images and offer wide apertures for low-light situations or creative depth of field effects.
- Tilt-Shift Lenses: Tilt-shift lenses are specialized lenses that allow you to control perspective and depth of field. They are commonly used in architectural photography but can also be useful in landscapes to correct converging lines or achieve a unique “miniature” effect.
- Filters: While not lenses themselves, filters are often used in landscape photography to control light and enhance the final image. Circular polarizers can reduce reflections and enhance colors, while graduated neutral density filters can help balance exposure between bright skies and darker landscapes.
When choosing a lens for landscape photography, consider factors such as the focal length that suits your style, the level of image quality you need, the weight and portability of the lens, and your budget. Some photographers prefer to carry a selection of lenses to cover various scenarios, while others opt for a single versatile lens that can handle a wide range of landscape situations. Ultimately, the choice of lens will depend on your creative vision and the type of landscapes you plan to capture.
Lens Models that are popular among landscape photographers due to their quality and suitability for capturing stunning landscapes:
- Canon EF 16-35mm f/4L IS USM: This lens offers a wide-angle focal range with image stabilization, making it ideal for capturing expansive landscapes with sharpness and detail. Canon offers a range of high-quality lenses that are well-regarded by landscape photographers.
- Nikon AF-S NIKKOR 14-24mm f/2.8G ED: Known for its exceptional optical performance, this lens is highly regarded for capturing wide vistas and intricate details.
- Sony FE 16-35mm f/2.8 GM: A wide-angle lens designed for Sony mirrorless cameras, offering excellent image quality and low-light performance.
- Fujinon XF 10-24mm f/4 R OIS: This lens is designed for Fujifilm X-series cameras and provides a versatile focal range for landscape photography.
- Tamron 17-35mm f/2.8-4 Di OSD: An affordable option with a wide-angle focal range, suitable for capturing landscapes with good image quality.
- Sigma 14-24mm f/2.8 DG HSM Art: Part of Sigma’s Art series, this lens is known for its sharpness and wide aperture, making it ideal for landscapes.
- Canon EF 24-70mm f/2.8L II USM: While not solely a wide-angle lens, the versatility and image quality of this lens make it a popular choice for landscapes, offering the ability to capture a variety of scenes.
- Nikon AF-S NIKKOR 24-70mm f/2.8E ED VR: Similar to the Canon counterpart, this lens offers versatility and image quality for a range of landscape scenarios.
- Sony FE 24-70mm f/2.8 GM: Another versatile option for Sony mirrorless cameras, offering excellent optics and low-light performance.
Remember that the choice of lens depends on your camera system and personal preferences. While wide-angle lenses are common for landscapes, some photographers also use prime lenses or telephoto lenses to create unique compositions. It’s important to consider factors such as image quality, focal length, maximum aperture, and any additional features like image stabilization when choosing a lens for your landscape photography.
2. Portrait Photography :
- Creating compelling portraits that showcase the personality and character of individuals. This can include traditional portraits, lifestyle photography, and environmental portraits.



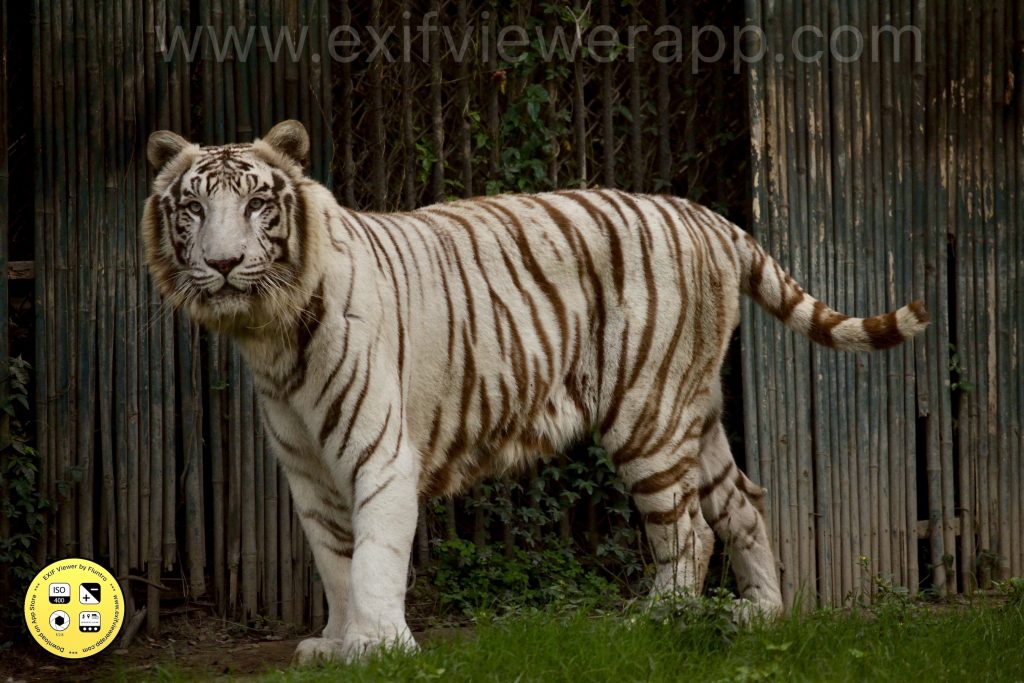
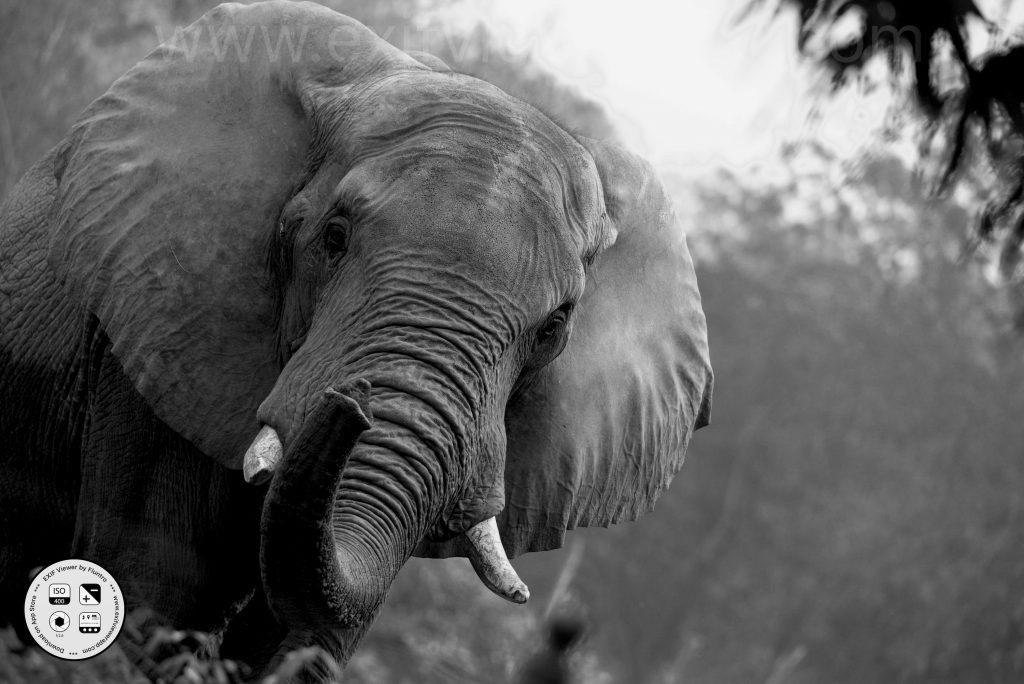
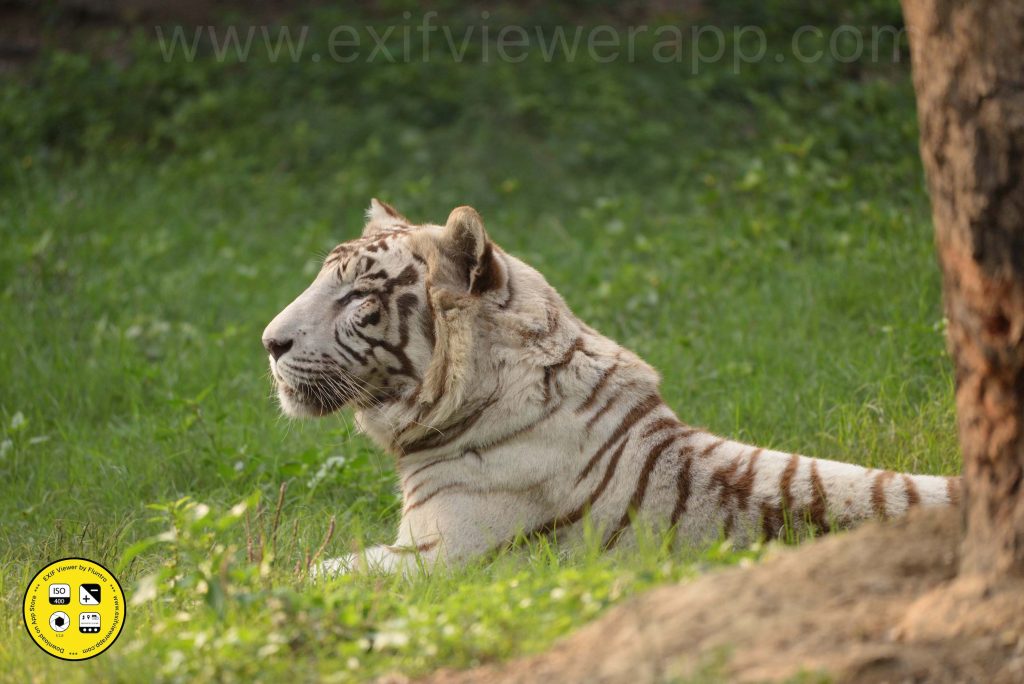
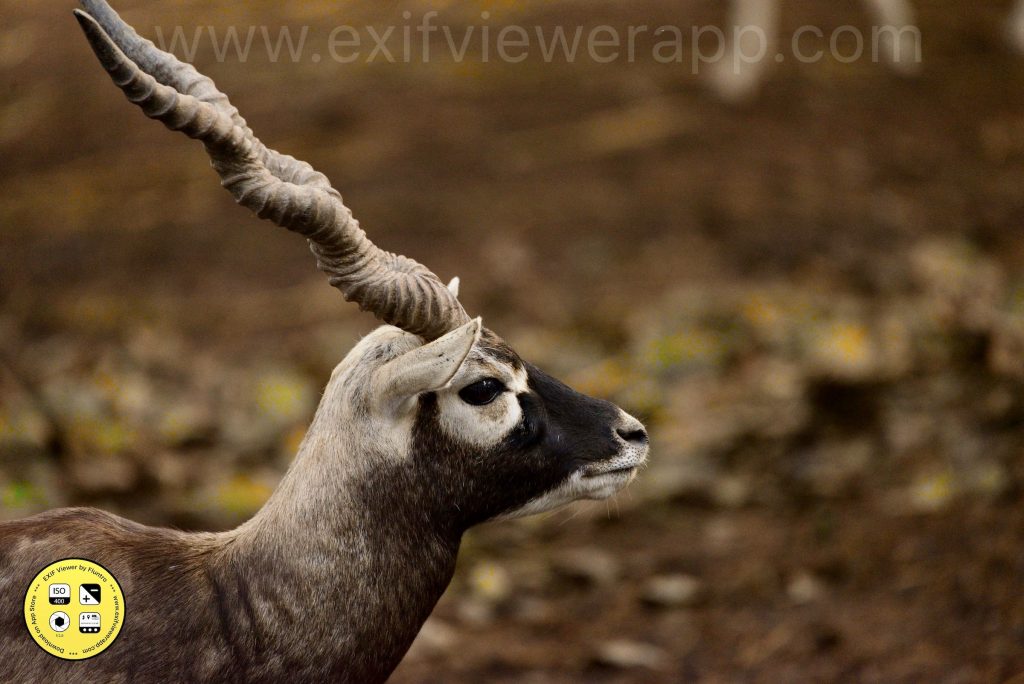
3. Wildlife Photography:
- Photographing animals in their natural habitats, from majestic mammals to tiny insects. This genre requires patience and understanding of animal behavior.




4. Macro Photography:
- Macro photography is a specialized genre of photography that focuses on exploring the world of small details capturing extreme close-up images of subjects, often revealing intricate details that are not easily visible to the naked eye. The primary goal of macro photography is to showcase the fine textures, patterns, and details of small subjects, such as insects, flowers, plants, textures, and other tiny objects. Using extention tubes are also gives you more detailed and macro images.
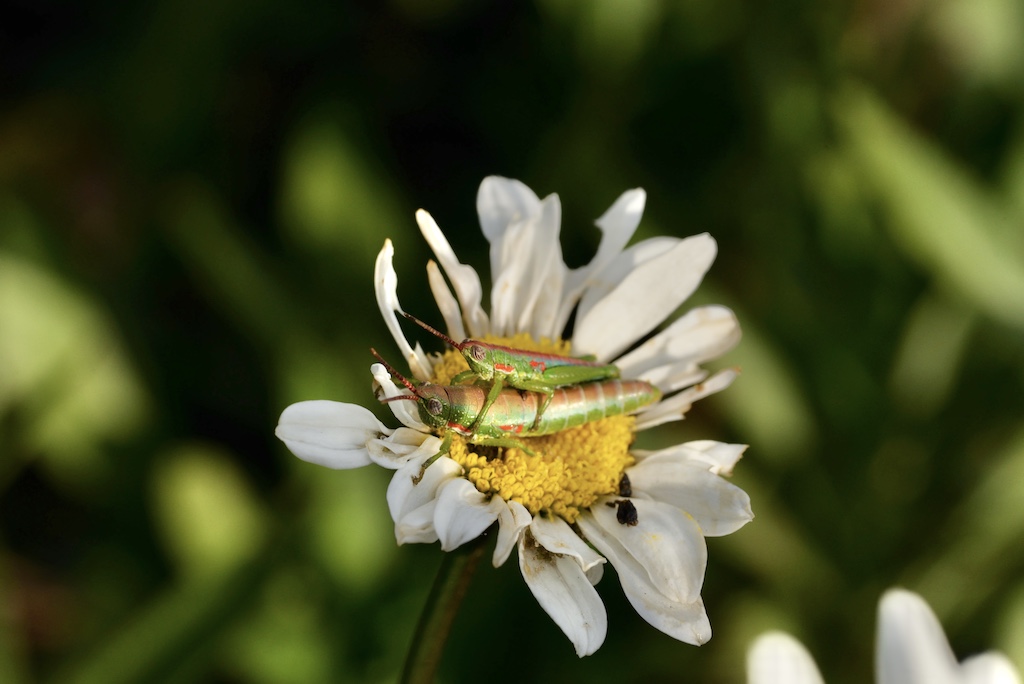
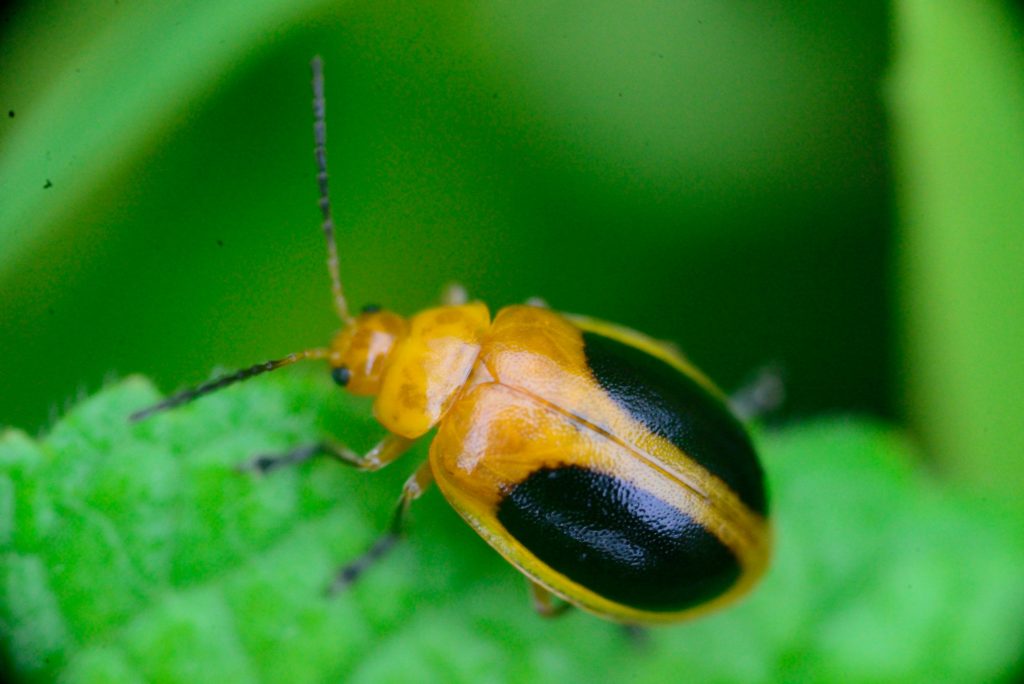
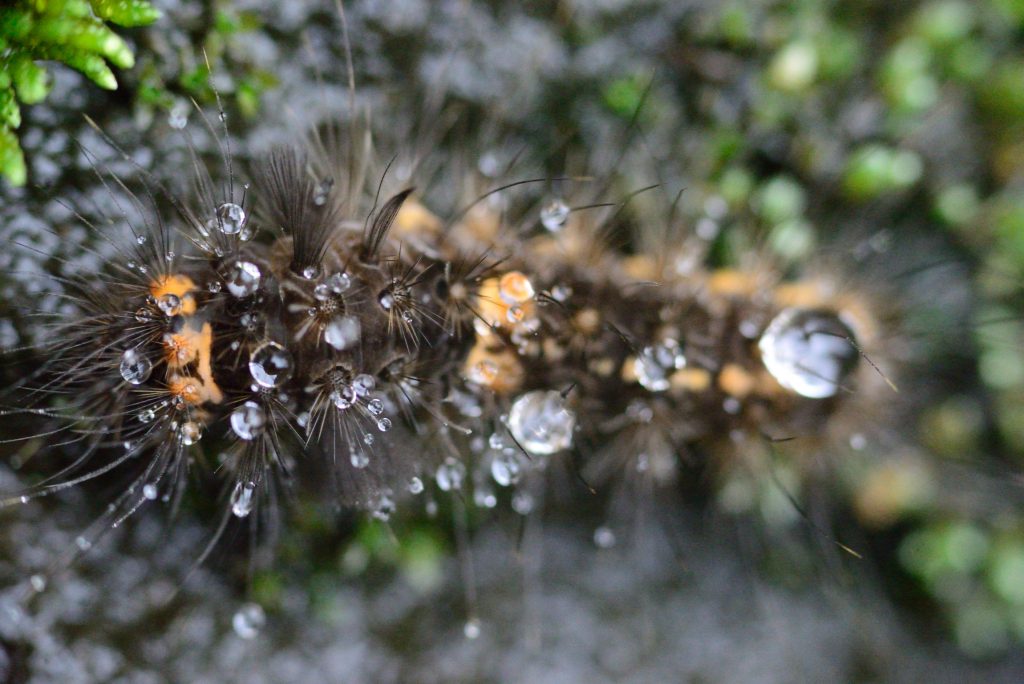
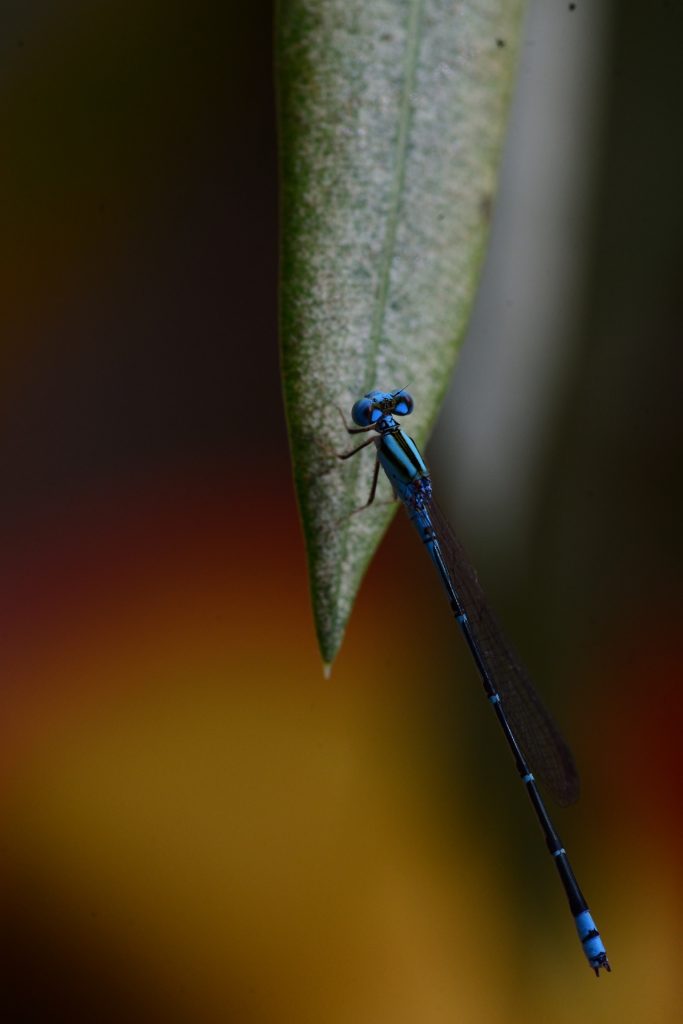
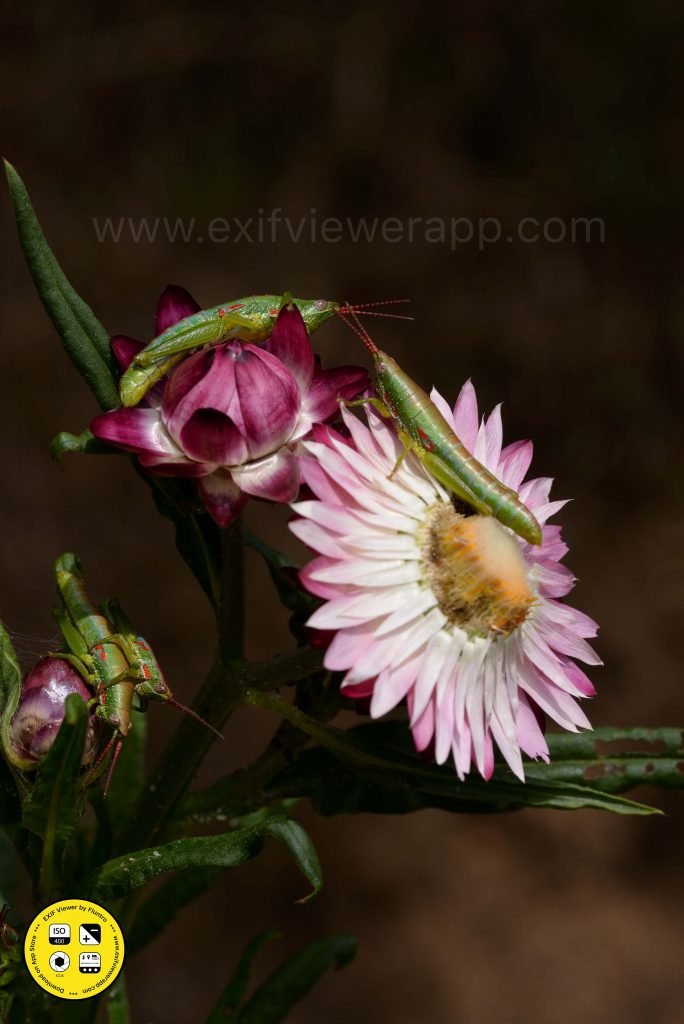





Key characteristics and techniques of macro photography include:
- Magnification: Macro photography involves achieving a high level of magnification to capture tiny subjects at a much larger scale on the camera sensor.
- Close Focus: Macro lenses or specialized equipment allow photographers to focus on subjects that are extremely close to the lens, often just a few centimeters away.
- Depth of Field: Due to the close proximity of the subject, achieving a sufficient depth of field can be challenging. Photographers often use small apertures (higher f-numbers) to increase the area in focus, but this can result in longer exposure times or the need for additional lighting.
- Lighting: Adequate lighting is crucial in macro photography. Natural lighting, diffusers, reflectors, and macro-specific lighting setups can be used to illuminate the subject and minimize shadows.
- Stabilization: Given the high magnification and potential for camera shake, using a tripod or other stabilization techniques is common to ensure sharpness in the images.
- Composition: Composition is important in macro photography just as it is in other genres. Photographers focus on arranging the elements within the frame to create visually appealing and engaging images.
- Background: Paying attention to the background is essential to avoid distractions and ensure that the subject remains the main focal point.
- Manual Focus: Due to the extremely narrow depth of field, manual focusing is often preferred to ensure precise control over what is in focus.
- Patience and Precision: Macro photography requires a lot of patience and precision. Minor movements can result in significant changes in focus and composition.
- Post-Processing: Editing software can be used to enhance colors, adjust contrast, and remove imperfections while maintaining a natural look.
5. Astrophotography:
- Photographing celestial objects such as stars, planets, and galaxies, often requiring specialized equipment and techniques.
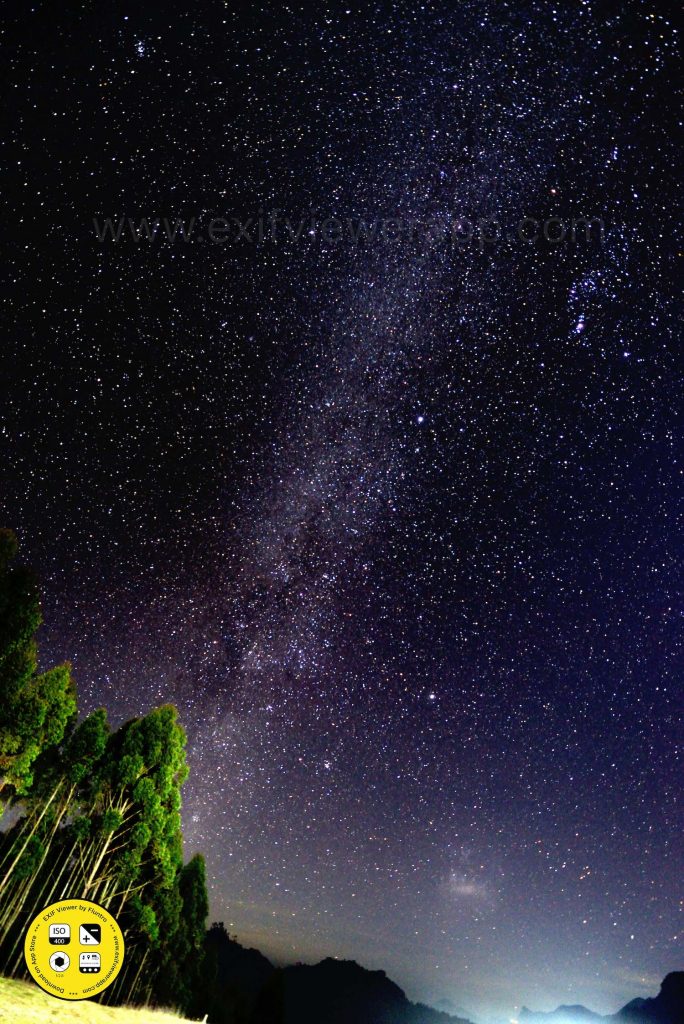

6. Black and White Photography:
- Focusing on monochromatic imagery to emphasize contrast, texture, and the interplay of light and shadows.
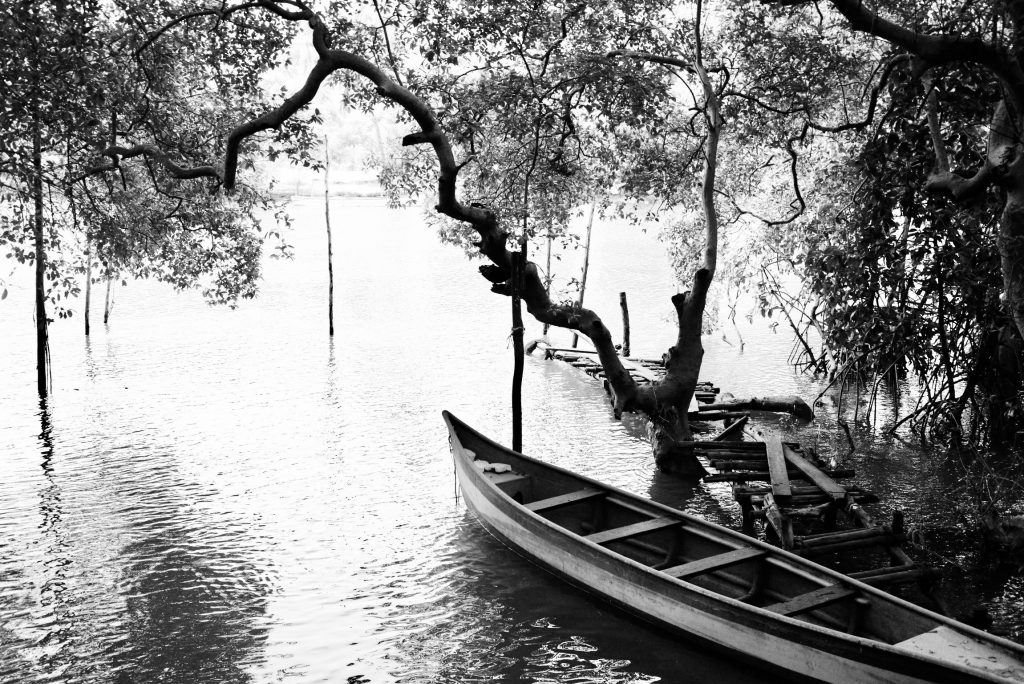


7. Food Photography:
- Capturing delicious dishes, ingredients, and culinary creations in visually appealing ways, often used in menus, cookbooks, and social media.
8. Street Photography:
- Capturing candid moments of everyday life in urban environments. Street photography often tells stories about people, cultures, and the dynamics of city life.
9. Travel Photography:
- Documenting your journeys and adventures, capturing the essence of different cultures, places, and landmarks.
10. Sports Photography:
- Capturing action-packed moments in sports events, showcasing the energy, athleticism, and emotion of athletes.
11. Architecture Photography:
- Focusing on buildings, structures, and urban environments, capturing unique angles, lines, and perspectives.

